Impact of Potato Preparation on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes

Learn how different methods of preparing potatoes influence the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and discover healthier dietary substitutions to reduce this risk.
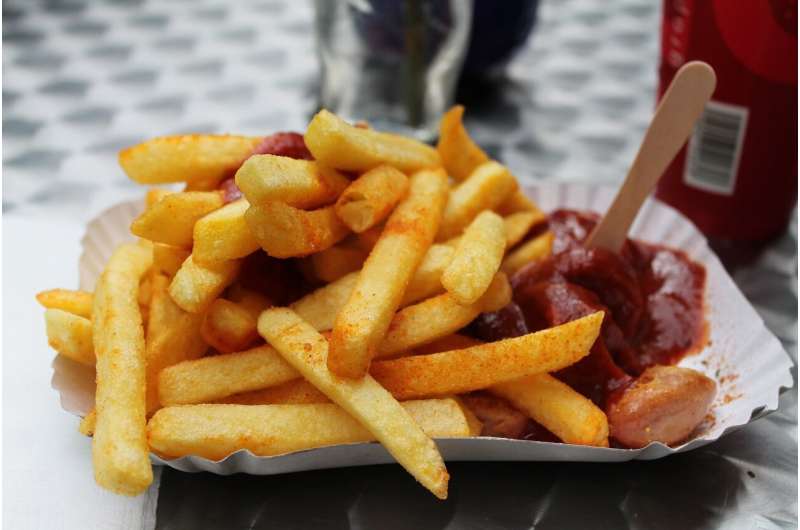
Recent research indicates that the method of preparing potatoes significantly influences their impact on the development of type 2 diabetes (T2D). A comprehensive study involving over 205,000 adults tracked dietary habits over several decades and found a notable association between consumption of French fries and an increased risk of T2D. Specifically, consuming three servings of French fries weekly was linked to a 20% rise in diabetes risk. Conversely, other preparation methods such as baking, boiling, or mashing did not show a significant connection with T2D.
The study highlighted that substituting potatoes with whole grains, like whole grain bread or pasta, could reduce the risk of developing T2D by approximately 4%. More notably, replacing French fries with whole grains could decrease the risk by nearly 19%. Interestingly, replacing refined grains with French fries was also associated with a lower risk, which underscores the complexity of dietary impacts on health.
This research underscores the importance of not only the type of food consumed but also the cooking methods used. The findings suggest that limiting fried potato products and choosing healthier, whole-grain options can be effective strategies in diabetes prevention.
The study was published in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) and sanctioned through rigorous peer review. It builds on previous data from multiple cohort studies involving over 500,000 participants across four continents, offering a clear message: small but meaningful dietary modifications—such as reducing fried potato intake and prioritizing whole grains—can substantially lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
As noted by Dr. Walter Willett, a leading epidemiologist involved in the research, public health efforts should focus on the specific preparation methods of foods and what they are substituted with, moving beyond broad food categories. This nuanced approach can inform more effective dietary guidelines to combat the rising prevalence of T2D.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Timing of Evening Meals Crucial for Blood Sugar Regulation in Prediabetes, Study Finds
Emerging research highlights the critical role of evening meal timing in regulating blood sugar levels for prediabetic individuals, paving the way for personalized dietary strategies to prevent diabetes.
Processed Foods and Sugary Drinks May Negatively Affect Brain Health Among Older Adults
Consuming processed meats and sugary beverages like soda may accelerate cognitive decline in older adults. New research emphasizes the importance of nutritious, minimally processed foods to support brain health as we age.
Increased Consumption of Ultra-Processed Foods Associated with Higher Lung Cancer Risk
A new study links high intake of ultra-processed foods to an increased risk of lung cancer. Reducing consumption of these foods may help lower the disease's burden globally.
Can Eating Broccoli Reduce Your Risk of Colon Cancer?
Discover how incorporating cruciferous vegetables like broccoli into your diet may help reduce the risk of colon cancer and promote gut health with practical tips from experts.