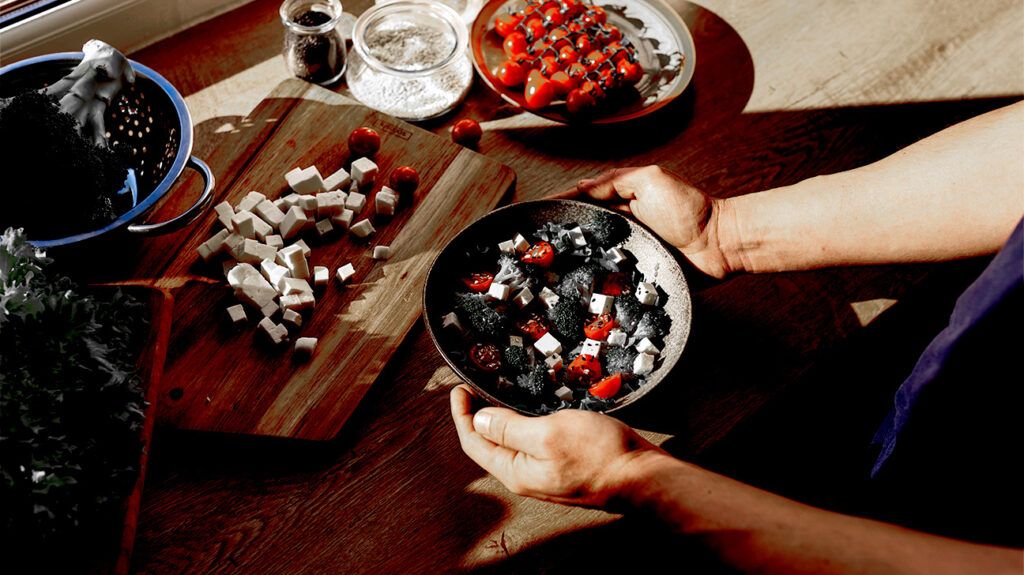
Anti-Inflammatory Diet May Boost Survival in Stage III Colon Cancer Patients
New research suggests that adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, along with regular physical activity, may improve survival rates for patients with stage III colon cancer. The study highlights the importance of diet in post-treatment outcomes.
Recent research from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute highlights the potential impact of dietary patterns on outcomes for patients with stage III colon cancer. In a Phase III clinical trial, individuals who adhered to an anti-inflammatory diet after treatment exhibited longer overall survival compared to those consuming a proinflammatory diet. This diet typically includes foods like vegetables, leafy greens, coffee, and tea, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Conversely, proinflammatory diets often contain high levels of red and processed meats, refined grains, and sugar-sweetened beverages.
The study, presented at the 2025 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, also emphasized the role of physical activity. Patients engaging in higher levels of weekly physical activity, such as walking regularly for an hour at a moderate pace, demonstrated significantly better survival outcomes. Importantly, the benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet persisted regardless of whether patients took celecoxib, an anti-inflammatory medication, suggesting that diet itself may play a crucial role in improving prognosis.
The trial involved 2,526 enrolled patients, with 1,625 completing detailed dietary and lifestyle questionnaires. Researchers calculated dietary inflammatory scores based on food intake, discovering that patients with the most proinflammatory diets faced an 87% higher risk of death than those with the least inflammatory diets. This aligns with previous findings linking systemic inflammation to colon cancer progression.
Dr. Sara Char, the study’s lead author, explained that these findings add to the growing evidence that diet and lifestyle modifications could be vital in post-treatment care. The research also points to the need for personalized dietary guidance and further exploration of biological mechanisms behind diet’s impact on cancer survival.
Overall, combining an anti-inflammatory diet with increased physical activity could significantly lower the risk of mortality in stage III colon cancer patients. The study opens the door for tailored lifestyle interventions aimed at improving long-term outcomes in colon cancer management.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-06-anti-inflammatory-diet-survival-treatment.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Low-Fat Vegan Diet May Enhance Weight Loss Compared to Mediterranean Diet
Recent research indicates that a low-fat vegan diet may promote greater weight loss than the Mediterranean diet, partly due to lower dietary acid load and its health benefits.
Innovative Food-Oriented Large Language Model Enhances Nutritional and Culinary Applications
Discover FoodSky, a cutting-edge large language model designed to enhance culinary and nutritional applications through advanced data management and retrieval techniques.
Global Efforts Fall Short in Reducing Childhood Wasting Worldwide
Despite global efforts, childhood wasting remains a critical issue with only 19% of countries on track to meet reduction targets. Effective nutritional interventions are vital to improve child health outcomes worldwide.
The Rapid Impact of Fatty Meals on Gut Health and Inflammation
Recent research reveals how high-fat meals can quickly weaken gut defenses and promote silent inflammation, increasing the risk of chronic inflammatory diseases over time.



