Understanding hMPV: A Key Respiratory Virus This Winter

Learn about human metapneumovirus (hMPV), a common but often overlooked virus causing winter respiratory illnesses. Discover symptoms, transmission, and prevention measures for this seasonal threat.
As the winter months arrive in Australia, there is a noticeable increase in respiratory illnesses, extending beyond the well-known culprits like COVID-19, influenza, and RSV. Amid these seasons of heightened viral activity, scientists are paying closer attention to human metapneumovirus (hMPV), a virus that has been circulating for some time but is now recognized for its significant impact on respiratory health.
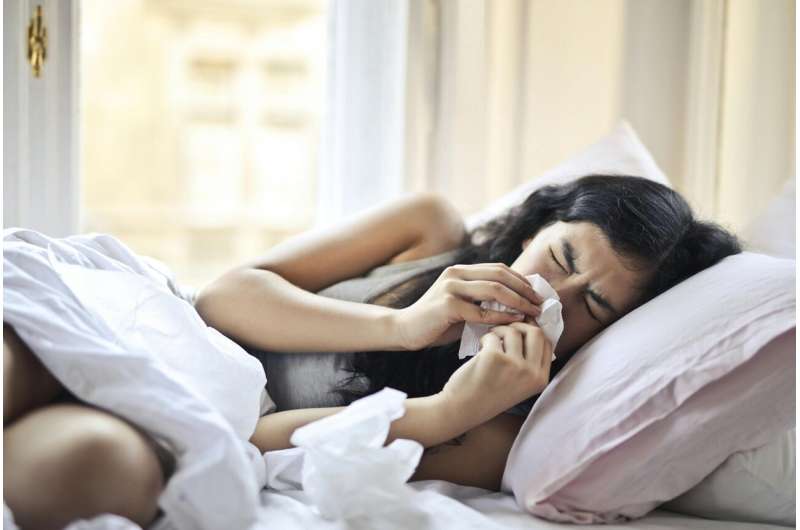
hMPV is a close relative of RSV and primarily infects the respiratory tract, causing symptoms similar to other respiratory viruses such as cough, fever, sore throat, and nasal congestion. Most individuals recover within about a week, experiencing mild illness. However, in vulnerable groups—including infants, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems—hMPV can cause severe conditions like bronchiolitis and pneumonia, often requiring hospitalization.
Transmission of hMPV occurs similarly to influenza and COVID-19, mainly through tiny droplets expelled during coughing or sneezing, and by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face. Most people are likely to encounter the virus multiple times throughout their lives, as immunity wanes over time, allowing for repeated infections.
Seasonally, hMPV tends to peak during winter and spring. Recent data from China, the USA, and Australia indicate an uptick in cases, underscoring the importance of monitoring this virus. In Australia, most hMPV data are gathered through voluntary surveillance by medical clinics, with around 7.8% of patients with respiratory symptoms testing positive for hMPV in late 2024. It ranks behind RSV, COVID-19, influenza, and rhinovirus in prevalence.
Currently, there are no specific vaccines or antiviral treatments for hMPV. Management involves supportive care, including rest, hydration, and medications like paracetamol or ibuprofen to alleviate symptoms. Severe cases, especially in children with difficulty breathing, require urgent hospital care.
Research efforts are underway by pharmaceutical companies such as Moderna, Pfizer, and Vicebio to develop vaccines. Until then, the best preventive strategies include practicing good hygiene—washing hands frequently, covering coughs and sneezes, cleaning shared surfaces, staying home when sick, and wearing masks in crowded indoor spaces.
Understanding and recognizing hMPV’s role in seasonal respiratory illnesses can help with early diagnosis and management, ultimately reducing the burden of winter respiratory infections.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Impact of Regulatory Changes on Food Safety and E. coli Outbreak Response
Recent policy shifts and reduced food safety oversight under the Trump administration have compromised the response to E. coli outbreaks, risking more public health crises. Learn about the implications of deregulation on food safety.
Maternal Microbes Influence Early Brain Development, New Research Finds
Emerging research reveals that maternal microbes play a vital role in early brain development, affecting regions responsible for stress and social behavior, with implications for obstetric practices.
How Brain Fluid Dynamics Influence Cancer Spread and Potential Strategies to Halt It
New research uncovers how cerebrospinal fluid flow in the brain influences medulloblastoma spread and explores promising strategies to inhibit tumor metastasis, paving the way for innovative treatments.
Retinal Damage Risks After the 2024 Solar Eclipse: Understanding the Hidden Price
The 2024 solar eclipse led to permanent retinal injuries in some viewers due to unsafe observation methods. Learn about the risks, symptoms, and importance of eye protection during solar events.