Long-Term Eczema Treatment Shows Benefits for Patients with Delayed Response
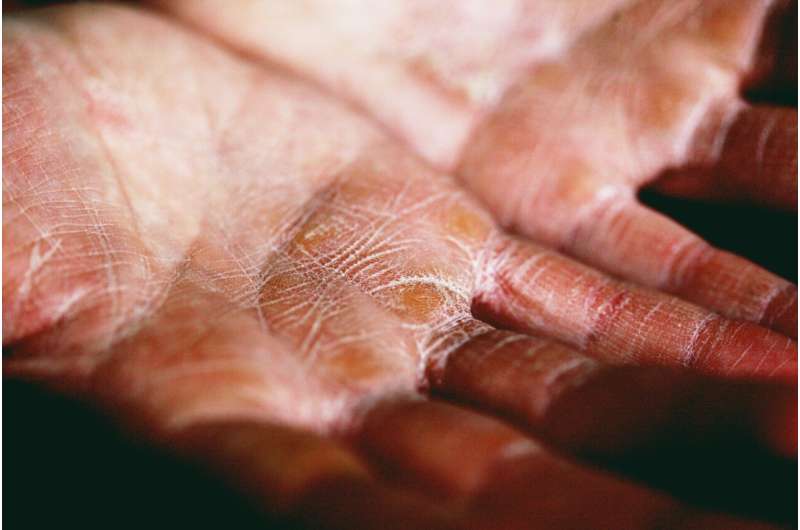
New research reveals that extended use of biologic treatments like lebrikizumab can significantly improve eczema symptoms even in patients with delayed response, supporting personalized treatment approaches.
Recent research from the Kimberly and Eric J. Waldman Department of Dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has shed light on the effectiveness of extended biologic treatment for patients suffering from moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema. The study emphasizes that individuals who do not exhibit immediate improvement after initial treatment sessions can still achieve significant health benefits with continued therapy.
Published in the latest issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, the findings highlight the potential of prolonged use of lebrikizumab, a biologic drug that targets the inflammatory pathway involving interleukin-13 (IL-13). IL-13 is a protein that contributes to the intense itching, redness, and skin damage characteristic of eczema. The study demonstrates that patients who did not respond strongly by 16 weeks of treatment often showed substantial improvement at 52 weeks.
Lebrikizumab works by blocking IL-13, helping to reduce inflammation and the symptoms associated with eczema. The research analyzed data from two international clinical trials, revealing that while 38.1% of patients did not meet the strict response criteria at 16 weeks, 58.1% already experienced at least a 50% reduction in their Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) scores. By the end of 52 weeks, an impressive 75.5% of patients achieved a 75% improvement (EASI 75), 44.2% reached a 90% improvement (EASI 90), and many reported significantly less itching.
Dr. Emma Guttman-Yassky, the lead author, stated that this research supports adopting a more personalized approach to eczema treatment. It offers hope to patients who initially do not respond to biologics, emphasizing that persistence with therapy can lead to meaningful improvement. These findings suggest that healthcare providers should consider extending treatment duration beyond the typical early assessment period to optimize patient outcomes.
This study underscores the importance of patience and perseverance in chronic eczema management and highlights the potential for tailored treatment plans that extend over longer periods for those not responding initially. It paves the way for more individualized and effective care strategies in managing this challenging skin condition.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Scientists Question the Safety of a Promising New Anticancer Drug
Recent scientific findings challenge the safety and purity of a promising gold-based anticancer treatment, emphasizing the need for further safety evaluations due to the complex mixture of compounds produced during synthesis.
Gut Microbes Could Play a Protective Role Against Chemotherapy Side Effects
Emerging research suggests gut bacteria can reduce chemotherapy side effects, potentially leading to probiotic-based treatments to improve cancer therapy tolerability.
FDA Approves Targeted Therapy for Rare and Aggressive Blood Cancer Following Promising Clinical Trial Results
A groundbreaking clinical trial has led to FDA approval of pemigatinib for treating a rare and deadly blood cancer, offering new hope through targeted therapy and transplantation options.



