HIV Outbreak in Maine Highlights Risks of Policy Changes on Homelessness and Drug Use
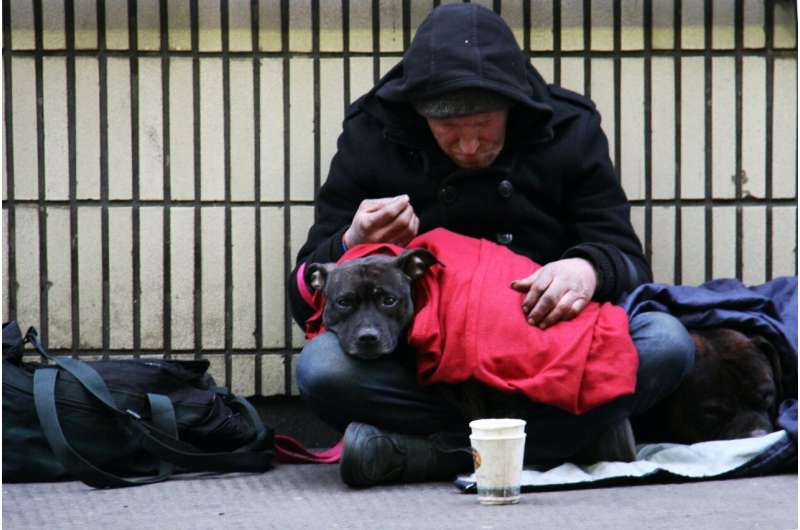

An HIV outbreak in Maine reveals how policy changes targeting homelessness and drug use can exacerbate public health crises. Experts warn that restricting harm reduction programs may lead to more infections and outbreaks. Read more about the implications for health and policy.
Penobscot County in Maine is currently facing the largest HIV outbreak in the state's history, with nearly all of the 28 identified cases over the past two years occurring among people experiencing homelessness and drug use. The city of Bangor, home to approximately 32,000 residents, has seen a severe spike in HIV infections, which public health officials attribute to factors like opioid addiction, housing shortages, and limited healthcare infrastructure.
A critical issue identified is the closure and shortage of sterile syringe programs, notably the recent shutdown of Health Equity Alliance (HEAL), which traditionally provided over half a million sterile needles annually to prevent disease transmission. The reduction in access to clean needles is believed to have contributed significantly to the outbreak. Experts highlight that without sufficient harm reduction measures like syringe services, HIV and hepatitis C infections tend to rise, and outbreaks become harder to control.
The outbreak predates the current political landscape but has gained attention because of recent federal policy shifts. The Trump administration's executive order aims to defund harm reduction programs, including syringe service initiatives, and promotes strict measures against homelessness, such as clearing encampments and forcing involuntary treatment, claiming these actions enhance public safety. Critics warn that such policies could worsen health crises by limiting access to essential services, which are proven to reduce disease spread and save lives.
Local advocates express concern that recent restrictions and closures hinder efforts to manage and prevent HIV outbreaks. They emphasize that harm reduction programs not only curb disease transmission but also reduce public disorder, with research showing they do not increase crime and are highly cost-effective.
In Bangor, the community has faced challenges balancing the need for public safety and humane treatment of vulnerable populations. The city has temporarily operated syringe exchange programs at designated sites, but zoning conflicts and political opposition have often hampered continuous service. Efforts are underway to improve outreach, including hiring case managers funded through opioid settlement funds, to reconnect with homeless individuals and those living with HIV.
The approach to homelessness also remains contentious. The recent clearing of encampments has left many untracked by social services, raising fears of further disease spread and overdose incidents. While officials claim to aim for balanced solutions, advocates argue more supportive, accessible harm reduction and housing strategies are necessary to prevent devastating outbreaks like Bangor’s.
As federal policies continue to focus on enforcement and containment, health experts warn that neglecting harm reduction and housing stability will likely lead to more health emergencies, echoing the lessons learned from recent outbreaks. Addressing social determinants of health remains critical in controlling infectious diseases among vulnerable populations.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-09-hiv-outbreak-maine-trump-crackdown.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Study Finds Watching Others Eat Can Encourage Overeating in Mice
New research presented at ENDO 2025 demonstrates that mice tend to eat more when they see others consuming tasty foods, revealing social and visual cues as factors in overeating. The study highlights the brain's reward system as a target for future obesity treatments.
Unexpected Foods Like Pea Protein and Buckwheat Can Cause Serious Allergic Reactions
Emerging research reveals that foods like pea protein and buckwheat, not currently on allergen labels, can trigger severe allergic reactions, emphasizing the need for regulatory updates to enhance food safety.
Germline Mismatch Repair Variants May Increase Risk of Uveal Melanoma
A recent study reveals that germline mutations in mismatch repair genes may predispose individuals to uveal melanoma, expanding our understanding of genetic risk factors associated with this eye cancer.
Detection of Measles Virus in Houston Wastewater Prior to Reported Cases
Early detection of measles in Houston wastewater samples before clinical cases highlights the potential of environmental surveillance as a powerful tool in public health for outbreak prevention.