New Insights on How Diet and Drink Can Affect Hair Loss
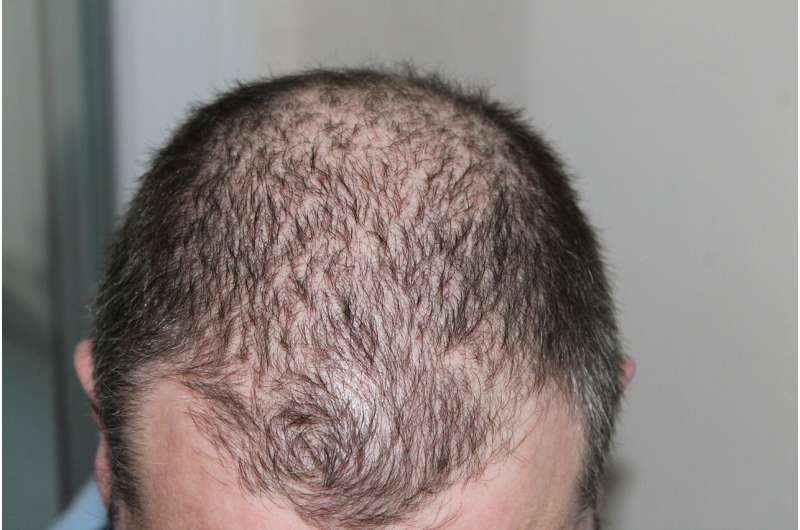
Discover how your diet and beverage choices can impact hair health. Learn about foods, nutrients, and supplements that support hair growth and prevent hair loss according to recent research.
Emerging research indicates that your dietary habits and beverage choices may play a significant role in hair health, potentially influencing whether your hair stays thick or begins to thin. Recent systematic reviews analyzing over 600,000 individuals have highlighted specific foods and drinks that can either promote hair growth or contribute to hair loss.
One key finding is that sugar-sweetened beverages and alcoholic drinks are linked to a greater risk of hair thinning. According to nutrition expert Laura Acosta, consuming high amounts of sugar triggers insulin spikes, leading to inflammation that can disrupt natural hair growth cycles. Alcohol, while not directly causing hair shedding, can impair nutrient absorption, stress the liver, disturb sleep, and evoke systemic inflammation—all factors that may hinder hair health.
Protein deficiency is another important aspect to consider. Adequate protein intake, roughly half a gram per pound of body weight daily, is essential for maintaining healthy hair. Deficiencies can result in hair thinning or loss, as noted by Miami-based specialist Dr. Jila Senemar, who emphasizes that diets lacking in protein, combined with hormonal imbalances, can exacerbate hair shedding.
Incorporating specific foods such as soy-based products like edamame and tofu, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower, may help reduce the risk of hair loss and support healthy growth. The antioxidants and phytochemicals in these foods, including isoflavones and carotenoids, have anti-inflammatory properties that benefit scalp health. Additionally, compounds like quercetin found in persimmon leaves can improve blood flow to the scalp, promoting thicker hair.
Furthermore, some supplements and nutrients have shown promise. For example, pumpkin seed oil has been associated with increased hair growth, possibly due to its ability to reduce dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair thinning. Vitamin D levels are also crucial; higher levels, around 2,000 IU, may protect against hair loss. Iron supplementation, especially when combined with vitamin C to enhance absorption, has aided women experiencing hair thinning. Adults should ensure sufficient intake of biotin (Vitamin B7) through foods like meats, eggs, nuts, and vegetables, although supplementation only benefits those with a deficiency.
Recent investigations into collagen supplements also show potential for supporting hair growth, reflecting the growing interest in holistic approaches to hair health. Overall, observational studies suggest that a balanced diet rich in specific nutrients and phytochemicals can influence hair vitality, though causation has yet to be firmly established.
These insights underscore the importance of a nutritious, well-rounded diet not only for overall health but specifically for maintaining healthy, thriving hair.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-09-contribute-hair-loss.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Influence of Age and Gender on Food Choices and Dietary Patterns
A groundbreaking study reveals how age and gender influence food choices and dietary diversity, emphasizing the importance of personalized nutrition for health promotion across generations.
Understanding the Distinction Between Barista Milk and Regular Milk
Discover the key differences between regular milk and barista milk, including their formulation, foaming capabilities, and best uses for coffee lovers and baristas alike.



