Innovative Brain Organoids Shed Light on the Neural Roots of Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder
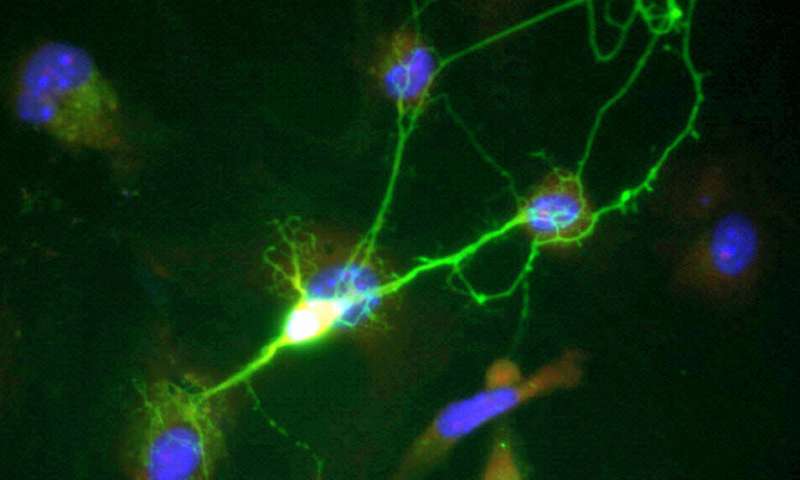
Lab-grown brain organoids are uncovering the neural activity patterns associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, paving the way for more accurate diagnosis and personalized treatments.
Recent advancements in neuroscience have introduced the use of lab-grown brain organoids that mimic human brain tissue, providing new insights into psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. These miniature, pea-sized brain models have revealed unique neural firing patterns associated with these mental health disorders, which are notoriously difficult to diagnose due to their complex and subtle neural signatures.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University engineered these organoids by converting blood and skin cells from patients diagnosed with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and healthy controls into stem cells capable of developing into brain-like tissue. Using sophisticated machine learning algorithms, they analyzed the electrical activity of the neurons within these organoids. Distinct electrophysiological behaviors emerged, allowing the team to classify organoids with an accuracy of 83%, which increased to 92% after applying subtle electrical shocks to stimulate neural responses.
This electrophysiological signature, characterized by intricate spikes and alterations at various intervals, appears to serve as a biomarker for these disorders, potentially enabling more precise diagnosis than current methods. To simulate brain network activity, the organoids were placed on microchips fitted with multi-electrode arrays, resembling mini EEGs. These organoids, which reach about three millimeters in diameter, contain diverse neural cell types and myelin, reflecting key aspects of the human prefrontal cortex involved in reasoning and cognition.
While the study involved a small sample size of 12 patients, the findings hold significant potential for clinical application. The team is now collaborating with clinicians to incorporate blood samples from psychiatric patients to test how various drug concentrations may influence neural activity in organoids. Such testing could streamline the process of finding effective treatments, reducing the current trial-and-error approach that can take months.
Dr. Annie Kathuria, the lead researcher, highlighted that this approach might help identify personalized medication strategies, especially for resistant cases like those unresponsive to drugs like clozapine. Ultimately, these advancements could revolutionize how psychiatric disorders are diagnosed and treated, moving toward a more targeted and efficient methodology.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-09-brain-organoids-reveal-potential-neural.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Long-Term Impact of War Zone Deployment on Soldiers' Partners and Cognitive Function
Deployment to combat zones can have lasting effects on soldiers' cognitive health and significantly increase stress levels in their partners, emphasizing the need for targeted family support and mental health interventions.
Consuming More Fruits and Vegetables Can Mitigate Poor Sleep Effects on Mental Well-Being
Increasing fruit and vegetable intake alongside good sleep and physical activity can improve mental well-being in young adults, even after poor sleep, according to recent research.
Using Mindfulness Techniques to Help Expectant Parents Manage Stress During Parenthood
Research shows that mindfulness-based childbirth and parenting classes can significantly reduce stress for expectant parents, especially those with higher anxiety, by fostering emotional resilience and stronger family support.
Teen Tobacco and E-Cigarette Use Linked to Higher Risks of Depression and Anxiety
Adolescent use of e-cigarettes and traditional tobacco products is linked to heightened risks of depression and anxiety, with dual use increasing these mental health challenges. A recent study underscores the importance of preventive measures and mental health support for teens.



