How Wegovy and Mounjaro May Impact Contraceptive Effectiveness
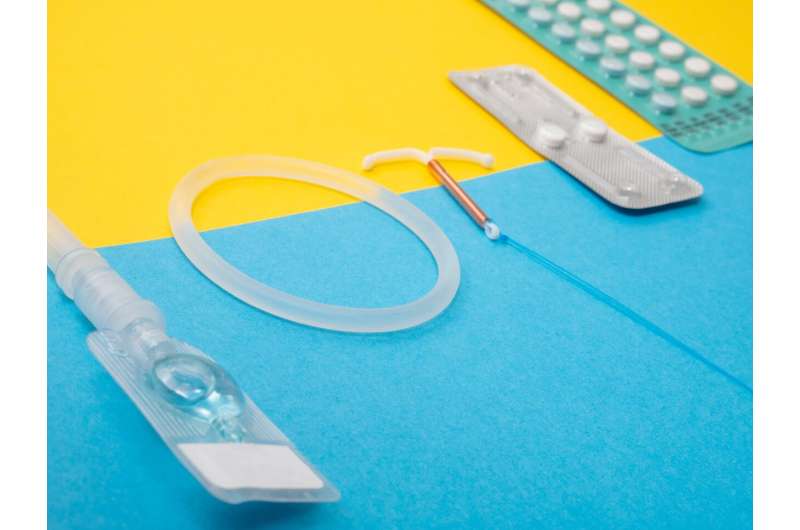

Recent studies indicate that weight loss drugs Wegovy and Mounjaro may reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives by altering drug absorption, necessitating additional contraceptive measures.
Weight management medications such as Wegovy (semaglutide) and Mounjaro (tirzepatide) are gaining popularity among individuals seeking to lose weight. However, recent concerns have emerged regarding their potential influence on the effectiveness of contraceptive methods, especially oral pills. The UK’s medicines regulator has issued guidance after reports of unintended pregnancies among women using these drugs.
These medications function by mimicking natural hormones like GLP-1 and, in the case of tirzepatide, GIP, hormones that play a significant role in suppressing appetite. They target brain regions associated with hunger and slow gastric emptying, which can alter how quickly the stomach empties and how other medications are absorbed.
A notable study from 2024 found that tirzepatide reduced the blood levels of ethinylestradiol—a common component of combined oral contraceptives—by 20%, and extended the time for absorption by two to four hours. This decrease in absorption efficiency can diminish the contraceptive's ability to prevent pregnancy. Semaglutide's impact appears less pronounced but might still influence drug absorption.
The altered gastric emptying caused by these drugs partly explains their effect on oral contraceptive efficacy. Additionally, side effects such as vomiting and diarrhea, which are common with GLP-1 medications, can further reduce absorption by expelling the medication before it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Women experiencing these side effects are advised to use a backup contraception, such as condoms, for at least four weeks after starting treatment.
Another factor to consider is weight loss itself, which has been linked to increased fertility. Obesity is associated with reduced fertility; thus, losing weight may improve reproductive function, potentially increasing the chances of pregnancy regardless of contraceptive use.
While non-oral contraceptives like IUDs, patches, or implants are unlikely to be affected due to their absorption pathways, women on oral contraceptives are encouraged to use additional protection during treatment with Wegovy or Mounjaro. If pregnancy occurs, consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended to explore alternative options.
Overall, these findings highlight the importance of discussing contraceptive plans with healthcare providers when starting weight management medications that influence gastric emptying. Continued research is needed to fully understand the interaction between these drugs and various contraceptive methods.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
AI Model Suggests Nearly 40% of Breast Cancer Patients Could Avoid Axillary Surgery
A groundbreaking AI model from Lund University predicts that nearly 40% of breast cancer patients could safely avoid axillary surgery, paving the way for more personalized and less invasive treatment strategies.
Artificial Sweetener Sucralose May Reduce Effectiveness of Cancer Immunotherapy
Emerging research indicates that the artificial sweetener sucralose may reduce the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy by altering gut microbiota and immune cell function. Learn what this means for cancer patients and their dietary choices.
Innovative Approach Estimates Measles Vaccination Coverage Without Recent Survey Data
A new modeling technique utilizes routine clinic data to estimate regional measles vaccination rates without relying on recent surveys, enhancing outbreak prevention efforts globally.
Balancing the Potential of Healthcare AI with Environmental Impact
A Cornell study introduces a framework to make healthcare AI more sustainable by reducing energy consumption and emissions, highlighting the importance of environmental considerations in health technology deployment.