Study Links Excessive Screen Time to Increased Heart Disease Risk in Youth
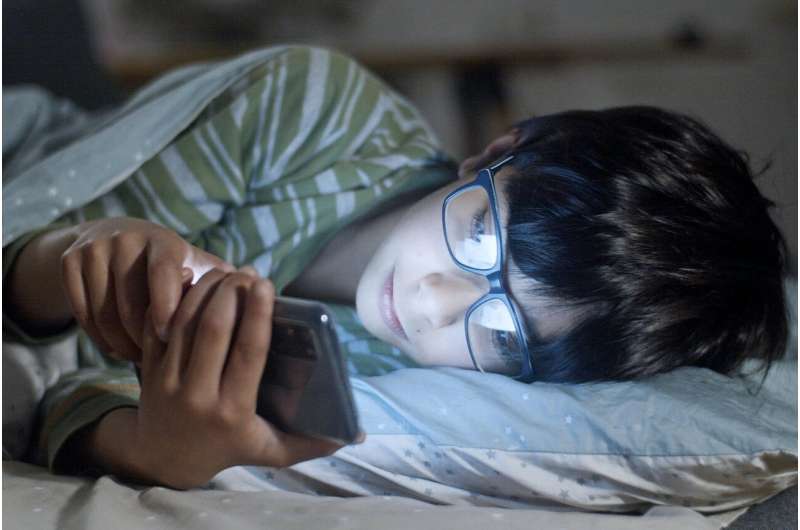

Extensive screen time in youth is associated with increased risk of heart and metabolic diseases, highlighting the importance of moderating device use for better long-term health outcomes.
Recent research from Denmark demonstrates a significant link between prolonged screen exposure and heightened risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases among children and adolescents. The study observed over 1,000 participants aged 10 to 18, analyzing their screen usage habits alongside sleep patterns to assess potential health impacts. Findings indicate that spending excess hours on devices like smartphones and televisions correlates with elevated markers for high blood pressure, cholesterol, and insulin resistance, which are precursors to heart disease and diabetes.
Lead researcher David Horner from the University of Copenhagen explained that each additional hour of daily screen time can increase a child's risk for these conditions by roughly a quarter to half a standard deviation. When considering this effect across a population, the potential for early-onset cardiometabolic issues becomes a serious public health concern. While experts debate the extent of screens' harmful effects, there's a consensus that youth are more vulnerable to these risks, emphasizing the importance of balanced habits.
This study underscores the growing necessity to monitor and limit screen exposure among young populations to promote healthier lifestyles and reduce future disease burden. For more detailed insights, consult the original publication in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
The Impact of Fans on Older Adults During Dry Heat: A Closer Look
Research highlights that using fans can help older adults stay cooler in humid heat, but may increase heat stress in dry conditions. Learn more about effective cooling strategies for seniors.
Breakthrough in Cancer Precision Therapy: Identifying Patients Who Benefit from Bexmarilimab
A new study unveils how bexmarilimab activates the immune system against cancer and introduces a gene signature for selective patient treatment, advancing personalized immunotherapy.
Advances in Whole Genome Sequencing Enhance Breast Cancer Treatment and Clinical Trial Matching
New research shows that whole genome sequencing can uncover genetic markers to personalize breast cancer treatment and improve clinical trial matching, potentially benefiting thousands of patients annually.