Rising Migration of Ticks Threatens Increased Disease Transmission Risks
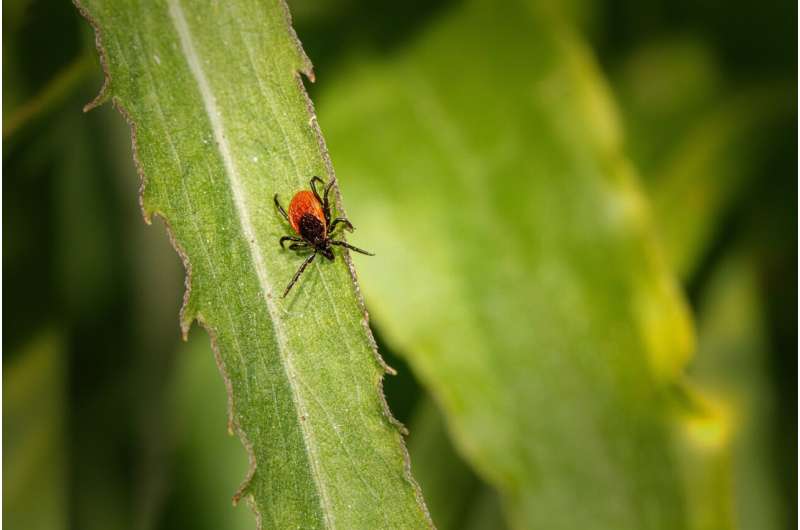

The migration of tick populations into new regions, driven by climate change, heightens the risk of tick-borne diseases. Monitoring efforts are vital for public health and disease prevention.
Recent studies highlight the alarming migration of tick populations into new regions, significantly elevating the risks of tick-borne diseases. As climate change shortens winter hibernation periods, ticks remain active for longer durations, enhancing their ability to hitch rides on wildlife, pets, and humans. Biologists such as Grant Hokit have been conducting field surveys in Montana, using simple yet effective tools to collect ticks from grasses and shrubs along hiking trails. These efforts have led to the discovery of deer ticks in Montana for the first time, a species notorious for transmitting Lyme disease. The spread of deer ticks and other species into new areas underscores the importance of monitoring and identifying these vectors to protect public health.
Understanding which tick species are present is crucial for healthcare providers, especially since not all ticks carry diseases. For example, the presence of deer ticks increases the likelihood of Lyme disease, while other ticks might carry different pathogens like Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Surveillance programs, including field collections and laboratory testing, are vital for mapping tick distribution and pathogen prevalence. However, funding limitations hinder comprehensive monitoring across all regions, often relying on passive reporting from residents, vets, and doctors.
In Montana, the state health department actively engages in tick surveillance, collecting specimens from various counties to assess potential health risks. Researchers analyze climate and vegetation data to predict where ticks could establish new populations, particularly in areas like the Flathead Valley. These measures aim to inform local populations and healthcare professionals about emerging tick threats and the potential for new disease outbreaks.
The increase in tick range due to climate factors emphasizes the need for ongoing research, better funding, and public awareness to mitigate future health risks associated with tick-borne diseases.
source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-09-migrating-disease-tracked-quickly.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
ISS Study Connects Astronaut Bone Loss to Stem Cell Changes in Microgravity
Research from the ISS reveals how microgravity affects stem cells, leading to bone loss in astronauts. This discovery has implications for osteoporosis treatment and space medicine.
Obesity's Impact on Concussion Recovery Even Among Athletes
New research reveals that higher BMI, including in athletes, is linked to worse concussion recovery due to increased inflammation, underscoring the importance of body health in injury management.
Emerging Tuberculosis Case Raises Public Health Concerns in Northern California
A recent case of contagious tuberculosis at a popular California casino has prompted health officials to conduct contact tracing, highlighting the ongoing risk and resurgence of TB in the region. Learn about symptoms, transmission, and prevention.