Long-Term Fatigue Can Persist for Up to a Year After a Mini-Stroke
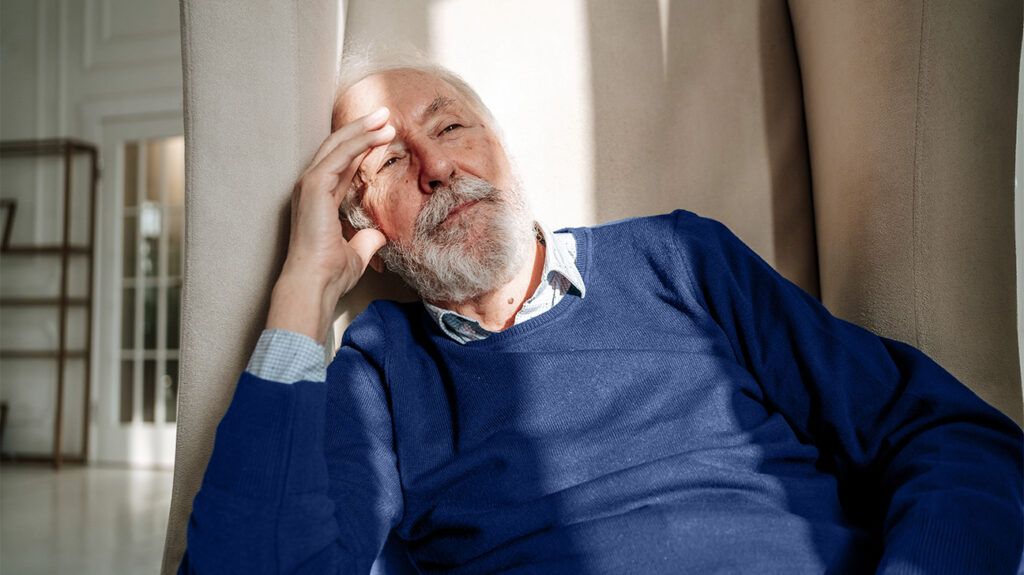

New research reveals that fatigue can last up to a year after a transient ischemic attack, highlighting the importance of follow-up care for TIA patients.
Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), commonly known as 'ministrokes,' can have lasting effects beyond the immediate neurological symptoms. Recent research indicates that more than half of individuals who experience a TIA may suffer from fatigue that persists for up to a year after the event. The study highlights the importance for healthcare providers to monitor and address fatigue in TIA patients, as it can significantly impact recovery and quality of life.
The research, published in Neurology and conducted by Danish researchers, involved tracking fatigue levels in patients shortly after their TIA and during follow-up visits at 3, 6, and 12 months. Results showed that over 60% of patients experienced pathological fatigue at the start of the study, with more than half continuing to report fatigue after a year. Interestingly, factors such as the presence of acute infarction or a history of anxiety or depression played a role in fatigue outcomes.
This study underscores the need to reconsider post-TIA care, emphasizing ongoing fatigue assessment and management. Healthcare professionals are encouraged to incorporate fatigue evaluations into follow-up protocols, as early identification and intervention could improve long-term outcomes. Experts suggest that rehabilitation and support should be extended to TIA patients similarly to stroke patients, given the comparable fatigue levels observed.
Continued research is necessary to understand why some individuals develop prolonged fatigue after a TIA, and how best to support recovery in these cases.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Mosquito-Borne Chikungunya Outbreak Spreads in Southern China
Southern China faces a rising outbreak of chikungunya, a mosquito-borne virus causing fever and joint pain. Authorities urge preventive measures to contain the spread.
Breast Implants and the Elevated Risk of Breast Lymphomas: What You Need to Know
New research reveals an increased risk of breast lymphomas, including ALCL, linked to implant-based reconstruction post-mastectomy. Explore the latest findings on safety and risk factors.
Real-Time Genomic Technology Enhances Detection of Golden Staph Resistance to Improve Treatment Outcomes
Innovative real-time genome sequencing is revolutionizing the detection of antibiotic resistance in golden staph infections, enabling personalized and more effective treatments.
Rethinking Myeloma: Advanced Bone Marrow Mapping Unveils Hidden Disease Complexity
Innovative spatial mapping of human bone marrow uncovers the complex microenvironment of multiple myeloma, challenging traditional treatment approaches and paving the way for personalized therapies.