Innovative Approach Enhances Quality of Life for Adolescents with Sickle Cell Disease
A new intervention developed by Columbia University shows promise in enhancing quality of life and treatment adherence among adolescents with sickle cell disease, highlighting innovative strategies for managing this chronic condition.
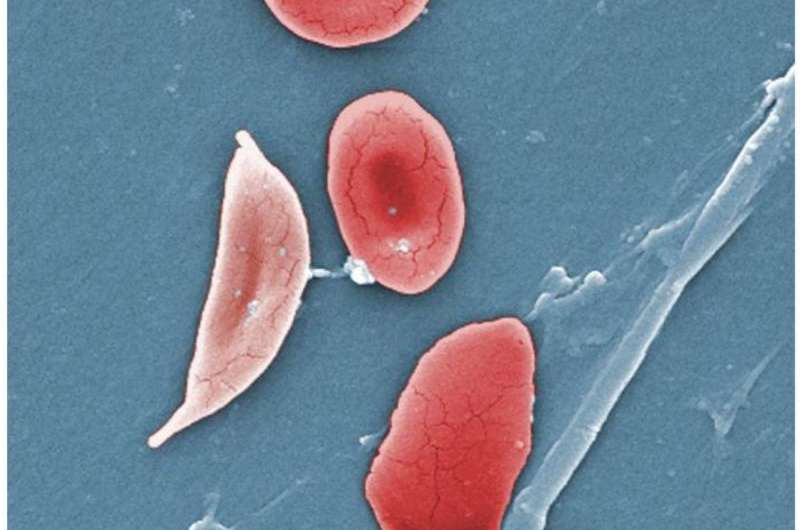
A groundbreaking intervention targeting adolescents with sickle cell disease has demonstrated promising results in improving their overall quality of life and adherence to vital treatment plans. Conducted by Columbia University School of Nursing, the study titled "HABIT Efficacy Trial Intervention Improves Elements of General and Disease-Specific Quality of Life in Youth with Sickle Cell Disease" highlights a novel strategy to support young patients in maintaining consistent hydroxyurea therapy.
Sickle cell disease affects around 100,000 individuals in the United States, with children constituting approximately 40% of those affected. The disease’s severity necessitates daily treatment with hydroxyurea, a medication that can reduce organ damage, alleviate pain, and decrease hospitalizations. Moreover, consistent medication adherence can enhance physical and mental well-being, along with allowing adolescents to keep up with their peers and daily activities.
However, due to the physical and psychological burden of sickle cell disease, many adolescents struggle to maintain regular treatment. To address this, researchers developed the Hydroxyurea Adherence for Personal Best in Sickle Cell Treatment (HABIT) trial. The study involved 50 adolescents aged 10–18, with participants speaking either English or Spanish, across four pediatric medical centers. Over 12 months, community health workers visited participants' homes to review educational materials, identify daily habits that support medication intake, and provide personalized text message reminders. Caregivers were involved during clinical visits to support adherence, and participants completed surveys at multiple points throughout the study.
Results indicated that the HABIT intervention notably improved certain aspects of participants’ quality of life, particularly mental health, around the nine-month mark. Nonetheless, these improvements were not sustained at the end of the study, signaling the need for further research to develop strategies that induce lasting behavioral change.
This approach emphasizes the importance of combining behavioral support and technology to enhance treatment adherence and quality of life in adolescents managing chronic illnesses like sickle cell disease.
Published findings from this trial contribute valuable insights into managing sickle cell disease more effectively and underscore the importance of ongoing support systems for young patients. Further studies are essential to identify more durable methods to improve treatment adherence and long-term health outcomes.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
What Your Pet's Feces Can Tell Us About the Spread of Antibiotic-Resistant Superbugs
A UK initiative is encouraging pet owners to send in pet feces for testing, helping monitor the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and protect public health.
Impact of the No Surprises Act: Significant Reduction in Patients' Out-of-Pocket Medical Expenses
A new study finds that the No Surprises Act enacted in 2022 has significantly lowered patients' out-of-pocket healthcare costs, saving nearly $600 annually per individual and reducing surprise billing among insured adults.
New Study Confirms Safety and Effectiveness of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy in Rabies Prevention
A recent clinical study confirms the safety and effectiveness of Rabishield, a monoclonal antibody treatment, in preventing rabies after animal bites, offering hope for better global rabies control.
Initiatives to Eliminate Race-Based Bias in Lung Function Testing
Efforts are intensifying to remove race-based adjustments from lung function testing, aiming for fairer and more accurate pulmonary assessments based on environmental and social factors. leading to updates in medical guidelines and disability evaluations.