Effective Communication Strategies Enhance Online Patient Engagement in Health Communities

Discover how targeted communication strategies can boost patient engagement in online health communities, with insights from a recent study on atrial fibrillation from the University of Amsterdam.
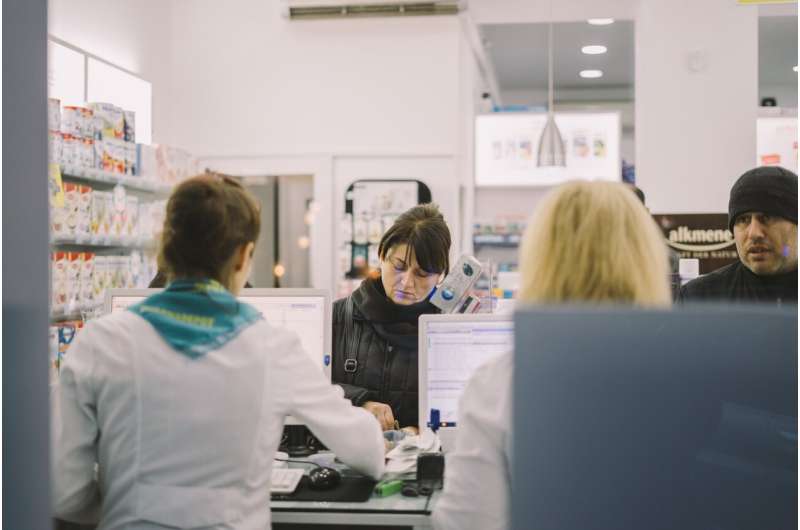
A recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Amsterdam and Amsterdam UMC sheds light on how targeted communication can significantly improve patient engagement in online health communities. Focusing on atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common irregular heartbeat disorder, the research demonstrates that specific messaging strategies can effectively raise awareness and encourage active participation.
The study involved a field experiment on Facebook and Instagram, where over 795,000 Dutch adults were exposed to 12 different communication concepts. These messages directed participants to the Atrial Fibrillation Innovation Platform (AFIP), an online community linking patients and healthcare professionals in cardiovascular health. The campaign resulted in over 18,400 visits, nearly 500 new subscriptions, and detailed engagement data.
Findings indicated that emotional tone and chosen topics are crucial in influencing user interaction. Fear-based messages emphasizing self-protection strategies drove higher click-through rates, while love-centered messages about family and connection increased both longer engagement times and subscriptions. Additionally, appeals from experts boosted interest in the community, and patient testimonials contributed to increased sign-ups and more prolonged site visits.
Myrthe Kuipers from the Amsterdam Business School highlights the practical implications of this research, stating, "Using marketing insights and data to tailor language and emotional appeals allows us to reach patients more effectively at different stages of their health journey. This can substantially improve the impact of online health platforms."
These insights are valuable for public health initiatives, digital health platforms, and policymakers aiming to create more effective online support and education tools for patients. The collaborative research team, including Dr. Umut Konus and Prof. İlker Birbil, worked with Prof. Bianca Brundel from Amsterdam UMC as part of the NWA-ORC 'CIRCULAR' consortium dedicated to advancing personalized AF treatments through patient involvement.
The full study, published in npj Digital Medicine, provides comprehensive guidelines on optimizing communication strategies to foster patient engagement in online health communities.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Preventing Medicine-Related Poisoning in Children: The Risks of Paracetamol and Safe Use
A new report highlights that nearly 100 children in Australia are hospitalized daily due to medication poisoning, with many incidents preventable through proper medication use and safety measures. Learn how to protect children from common medicine-related risks.
Success of Physician-Led HIV Care Pilot Boosts Testing and Treatment in London
A groundbreaking pilot in London demonstrated that physician-led HIV care significantly increases testing rates and improves treatment integration, paving the way for broader adoption of GP-led models in managing HIV as a long-term condition.
COVID-19 Infection Accelerates Blood Vessel Aging, Particularly in Women, Study Finds
New research shows COVID-19 infection accelerates blood vessel aging, especially in women, increasing cardiovascular risks. Learn about the study's findings and prevention strategies.