Innovative Breathing Device Promises Improved Survival for Sleep Apnea Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
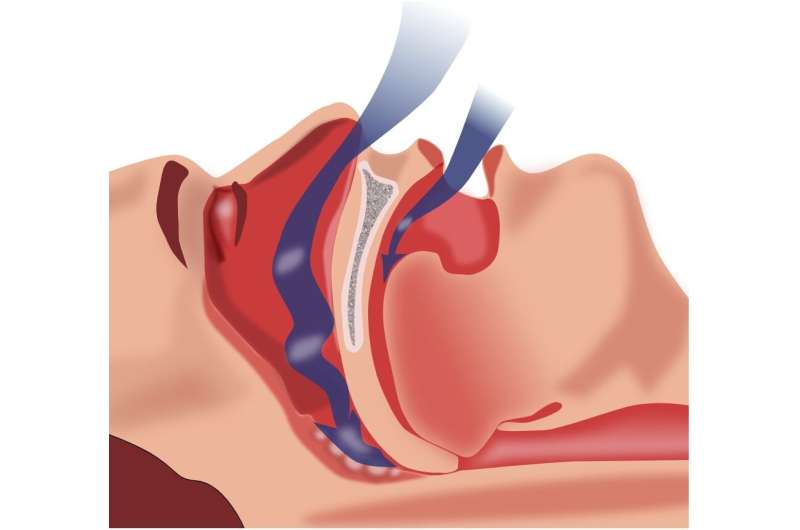
New research indicates that CPAP therapy may significantly improve survival rates in people with sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Recent research presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Annual Meeting in Vienna highlights the potential of a breathing therapy to significantly enhance survival rates among individuals suffering from both obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). The study underscores that treatment with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which keeps the airways open during sleep, may reduce the risk of death by approximately 26% in this high-risk population.
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the muscles in the throat relax during sleep, causing airway blockage and resulting in frequent awakenings and decreased oxygen levels. This condition not only disrupts restful sleep but also elevates the risk for serious health issues including high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and worsened diabetes control. Many cases remain undiagnosed, yet OSA is estimated to affect about 1 billion adults worldwide, with 50-80% of those with T2D also suffering from this sleep disorder.
The Swedish study analyzed data from five national registers encompassing over 750,000 T2D patients, comparing those prescribed CPAP therapy with those whose sleep apnea status was unknown or untreated. Results showed that individuals treated with CPAP were younger, had higher body mass index (BMI), and included fewer women. Remarkably, only 6.1% of the CPAP group died over 14 years versus 28.7% in the untreated group. After adjusting for factors like age, sex, cardiovascular history, BMI, smoking, kidney function, and medication, the researchers found that CPAP use was associated with a 26% reduction in the risk of death from any cause.
Dr. Jonas Agholme from Linköping University emphasized the importance of integrating sleep apnea management into diabetes care, noting that early diagnosis and treatment could substantially improve patient outcomes. However, he also highlighted that more rigorous, controlled studies are needed to establish a clear causal relationship between CPAP therapy and survival benefits.
While the findings are promising, they derive from observational data within the Swedish healthcare system, and further research is necessary to confirm applicability to broader populations. Nonetheless, this study adds to the growing evidence that addressing sleep-disordered breathing is crucial for enhancing the health and longevity of individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-09-device-profound-impact-survival-people.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Japan's Oldest Person at 114: Retired Doctor and Olympic Torchbearer
Meet Japan's oldest living person, 114-year-old retired doctor and former Olympic torchbearer Shigeko Kagawa, whose life exemplifies Japan’s remarkable longevity and active aging.
Unveiling HIV Persistence: How Minute Genetic Variations Influence Viral Replication and Latency
Research from UVA uncovers how small genetic changes in HIV influence its replication and ability to evade treatment, guiding future cure strategies.
Genetic Mutation in Ashkenazi Jewish Men May Increase Prostate Cancer Risk, New Research Finds
A recent study uncovers a specific genetic mutation in Ashkenazi Jewish men linked to a significantly increased risk of prostate cancer, opening new opportunities for personalized screening and treatment.
Tinnitus and Its Connection to Cognitive Decline in the Elderly
Chronic tinnitus in older adults is significantly associated with cognitive decline, highlighting the need for comprehensive assessments for elderly patients with tinnitus.



