Enhancing Longevity by Increasing Walking Speed: Experts Highlight Benefits
New research highlights that walking at a brisk pace for just 15 minutes daily can significantly reduce mortality risk, especially in underserved populations. Learn how increasing walking speed can enhance cardiovascular health and longevity.
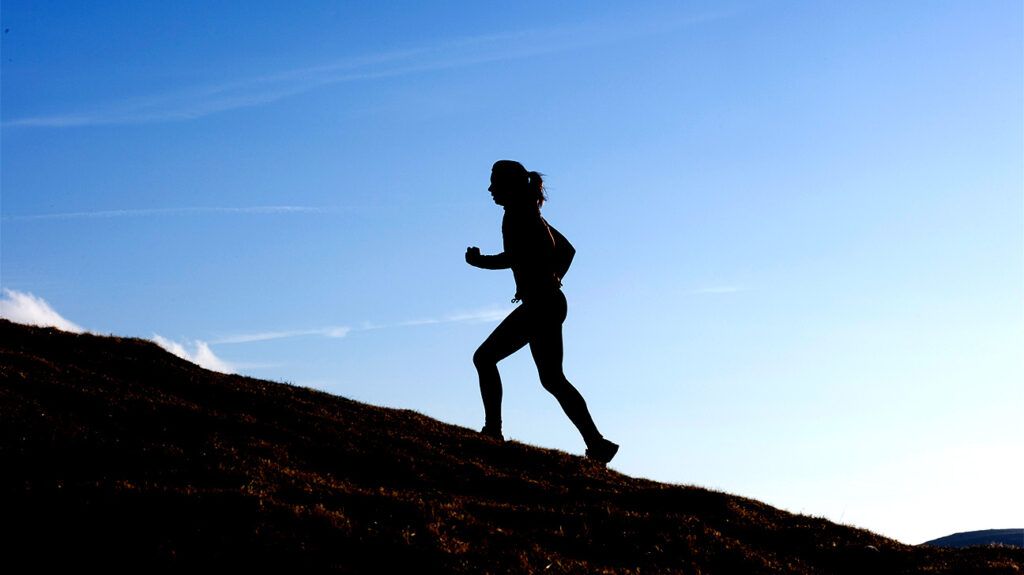
Regular walking is widely acknowledged for its positive impact on overall health and wellness. While much research has focused on middle-to-high income populations, recent studies emphasize the importance of walking pace, especially among underserved groups. A comprehensive analysis using data from the Southern Community Cohort Study, involving nearly 80,000 predominantly low-income and Black individuals across several southeastern US states, confirms that walking at a brisk pace offers significant health benefits.
Published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, the study underscores that walking quickly for just 15 minutes daily can reduce total mortality risk by approximately 20%. Even slower walking for over three hours a day demonstrated some protective effects. Importantly, these benefits persisted regardless of other physical activity levels, indicating that increasing walking intensity is a key factor in improving health outcomes.
The research found that fast walking notably decreased the risk of death from various causes, with the most substantial impact on cardiovascular diseases. This form of activity enhances cardiac output, boosts oxygen delivery, and strengthens heart function, all crucial for cardiovascular health. Additionally, it helps manage weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol, further reducing disease risk. Its accessibility makes fast walking an ideal, low-impact form of exercise suitable for all ages and fitness levels.
Low-income communities often face environmental and socioeconomic barriers such as limited access to safe walking spaces, unhealthy dietary options, higher smoking rates, and greater exposure to pollution. These factors contribute to increased disease prevalence and mortality, exacerbating racial health disparities. However, encouraging brisk walking can serve as an effective, cost-efficient intervention to mitigate some of these health disparities.
Lead researcher Wei Zheng emphasizes the importance of promoting quick walking in public health initiatives, particularly within vulnerable populations. Community programs that promote and support increased walking intensity could play a vital role in improving public health and lifespan. As Lili Liu, the study’s lead author, states, integrating strategies to increase walking speed can substantially reduce mortality rates and promote health equity across socioeconomic and racial lines.
In conclusion, adopting a faster walking pace is a simple yet powerful way to improve cardiovascular health and extend lifespan, especially among populations facing socioeconomic challenges. Public health policies and community efforts should emphasize this accessible activity to foster healthier, longer lives.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-07-pace-daily-boost-longevity-experts.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Do Compression Tights and Tops Enhance Exercise Performance and Recovery?
Learn whether compression tights and tops truly enhance exercise performance and aid recovery, supported by scientific research and expert insights.
Exercise May Be as Crucial as Medication in Preventing Colon Cancer Recurrence
Emerging research suggests that regular structured exercise may be as effective as medication in preventing colon cancer recurrence, offering a cost-effective and side-effect-free strategy to improve survival outcomes.
Reevaluating the 10,000 Steps a Day Goal: Fewer Steps Can Provide Similar Health Benefits
A comprehensive study suggests that walking 7,000 steps daily offers similar health benefits to the traditional 10,000-step goal, making physical activity more achievable for many individuals.



