The Potential of Mindfulness Practices to Improve Diabetes Management and Aid Long-Term Adherence
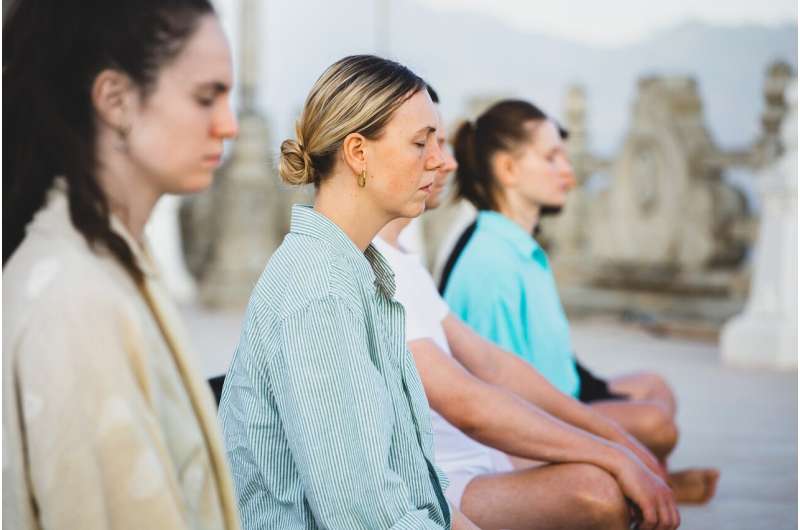

Research indicates that mindfulness practices may support individuals with type 2 diabetes by reducing stress and aiding long-term adherence to lifestyle changes, potentially improving blood sugar control.
Recent research from Australia suggests that mindfulness techniques could play a significant role in supporting individuals with type 2 diabetes in maintaining healthy lifestyle changes. A comprehensive systematic review published in Integrative Medicine Research analyzed data from 31 randomized controlled trials, involving 2,337 participants worldwide, to evaluate the impact of mindfulness interventions on managing the condition.
Type 2 diabetes, a chronic disorder affecting how the body processes blood sugar, impacts over 1.25 million Australians, with many remaining undiagnosed. Globally, nearly half a billion people are affected. If unmanaged, the disease can lead to severe health complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, blindness, and nerve damage.
Traditionally, diet and exercise modifications are central to managing type 2 diabetes. However, maintaining these lifestyle changes poses challenges for many, often due to stress, depression, or anxiety. Associate Professor Carolyn Ee from NICM at Western Sydney University highlights that these mental health issues can hinder consistent self-management.
The review explored whether mindfulness-based approaches—focused on moment-to-moment awareness and acceptance—could serve as a supportive strategy. These practices include mindfulness meditation, body scanning, mindful breathing, and mindful movement, which have been effective for various health conditions like depression, anxiety, addiction, and sleep disturbances.
Importantly, stress and mental health significantly influence blood sugar control. Elevated stress levels can disrupt sleep, alter diet, and reduce physical activity, all negatively impacting HbA1c levels, a key marker for blood sugar management. The study findings suggest that mindfulness practices may help decrease stress, depression, and anxiety, thereby potentially improving blood glucose regulation.
While more research is necessary to confirm long-term benefits, initial evidence indicates that mindfulness may not only help stabilize blood sugar levels but also lower blood pressure in people with type 2 diabetes. The researchers emphasize that integrating these practices with standard treatment could enhance overall disease management.
In summary, mindfulness interventions are a promising complementary approach to diabetes care, aiming to improve mental health and facilitate sustained health behavior changes. Continued investigation is essential to establish their full potential and develop clinical recommendations.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-05-mindfulness-link-interventions-people-diabetes.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Digital Mental Health Interventions Reduce Depression and Anxiety in Displaced Children
A recent study shows that brief, digital mental health interventions can effectively reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety in refugee youth, offering a scalable solution to support displaced children worldwide.
Growing Acceptance of Psychedelics Revealed in Large-Scale Social Media Study
A large-scale analysis of Reddit posts reveals increasing public acceptance of psychedelics, offering new insights into societal attitudes and potential therapeutic benefits of these substances. The study highlights the evolving perception of psychedelics in contrast to traditional illicit drugs.
Potential Impact of Medicaid Reductions on Mental Health Services in Rural America
Legislative Medicaid cuts threaten to reduce mental health care access in rural America, worsening disparities and increasing risks like suicide. Experts warn of closures and higher out-of-pocket costs impacting vulnerable communities.