Who Should Consider Screening for Skin Cancer?
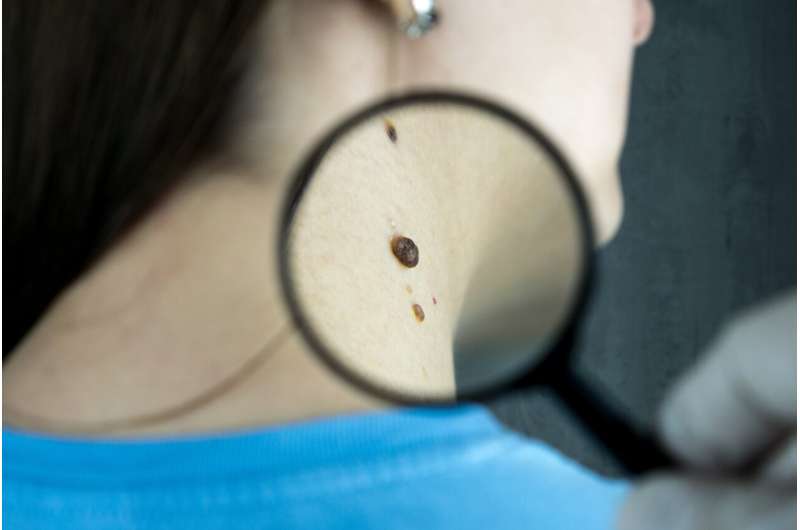
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the U.S., but early detection through regular screenings can save lives. Learn who should prioritize skin checks and how to identify warning signs of melanoma and other skin cancers.
Skin cancer stands as the most prevalent cancer in the United States, with over 6 million adults receiving treatment annually, according to dermatologist Dr. Michael Colgan from Mayo Clinic Health System. Among the various types, melanoma is particularly lethal due to its aggressive nature; in 2025, approximately 104,960 cases of invasive melanoma are projected to be diagnosed in the U.S., with about 8,430 fatalities. Fortunately, early detection of melanoma significantly improves survival rates, boasting a 99% five-year survival when caught early.
A common misconception is that only individuals with light skin or fair features are at risk for melanoma. Contrarily, melanoma can develop in people with darker complexions, often on extremities like hands and feet. These cases tend to be diagnosed at more advanced stages, leading to worse outcomes.
Regular skin checks are essential for everyone. Warning signs include new skin growths resembling moles, bumps, or scabs; rough patches; persistent sores; enlarging or discolored moles or freckles; and skin lesions that itch or cause pain. Performing simple self-examinations and consulting a dermatologist promptly can be life-saving.
Individuals with higher risk factors—such as a personal or family history of melanoma, age over 65, suppressed immune systems, tendency to burn easily, and light-colored eyes or hair—should prioritize regular skin evaluations. A brief dermatologist exam can detect abnormalities early and prolong life.
Early detection is key in managing skin cancer effectively. A quick, professional skin check can detect potential issues before they develop into serious health threats, underscoring the importance of routine screening for at-risk populations.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Innovative Targeted Radiation Therapy Achieves Near-Complete Response in Rare Sarcoma Cases
A new targeted radioligand therapy shows remarkable promise in treating rare solitary fibrous tumors, achieving near-complete responses in early clinical cases with minimal side effects. This innovative approach could revolutionize treatment options for malignantly transformed soft tissue sarcomas.
Revolutionizing Critical Care: Immune Cell Signatures as Guides for Treatment
Innovative blood tests analyzing immune cell gene signatures are set to revolutionize diagnosis and personalized treatment in critical care, enhancing outcomes for severely ill patients.
New Discoveries Reveal the Role of Iron Metabolism in Melanoma Cell Plasticity
New research uncovers the critical role of iron metabolism and organelle crosstalk in melanoma cell plasticity, highlighting potential targets for innovative cancer therapies.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Health Insurance Decisions
Artificial intelligence is increasingly used by health insurers to determine coverage and payments, raising concerns about transparency, fairness, and patient outcomes. Explore how AI influences insurance decisions and the ongoing regulatory challenges.



