Understanding Sports Hernias: Causes, Symptoms, and Management

Sports hernias are a common injury among athletes involving groin pain from overuse and twisting motions. Learn about causes, symptoms, and treatment options to aid recovery.
Sports hernias, also known as athletic pubalgia or Gilmore's groin, are a source of intense pain in the groin and lower abdominal region, primarily affecting athletes engaged in sports that involve rapid twisting, turning, and sudden movements. Unlike traditional hernias, sports hernias do not involve a protrusion of tissue through the abdominal wall but result from overuse and injury to the abdominal muscles, tendons, and surrounding tissues.
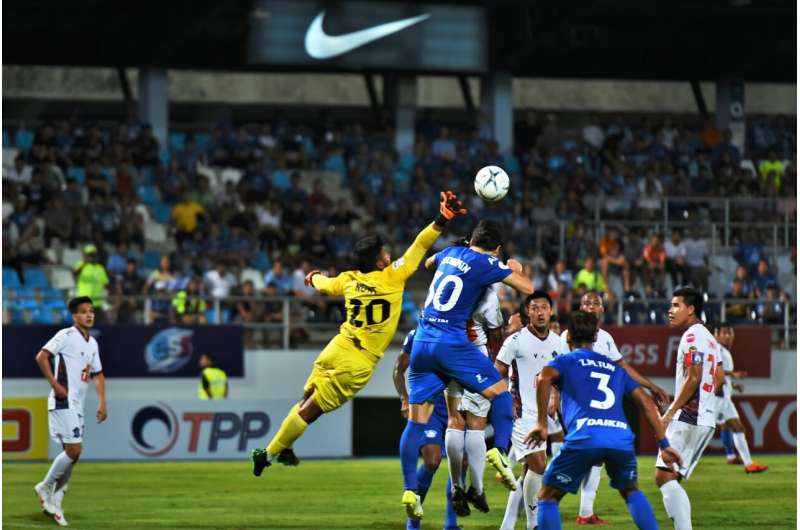
The condition was first described in the 1980s and is especially prevalent among footballers, although athletes in other sports such as hockey, wrestling, martial arts, skiing, rugby, and track events are also at risk. It is estimated that around 70% of sports hernias are related to sports activities, and groin pain can account for up to 18% of athletic injuries. Notably, males are up to nine times more likely to develop a sports hernia, partly due to differences in lower abdominal wall anatomy, including the passage of testes during fetal development that weakens the area.
Symptoms typically include persistent groin or lower abdominal pain, often exacerbated by physical activity. Men may also experience pain radiating to the genital area. Movements involving twisting, turning, or hip rotation—such as dribbling in soccer, hockey, or wrestling—can cause tears or shearing in affected tissues. The injury can occur from repetitive strain, especially at high speeds, or from sudden, forceful movements.
While sports hernias are most common in athletes, they can also happen to non-athletes who engage in heavy lifting, pivoting, or intense core exercises. For instance, improper lifting at job sites or aggressive gym routines involving deadlifts or medicine ball exercises may contribute.
Management of a sports hernia includes strengthening core and pelvic muscles through targeted training and physiotherapy, which can improve recovery. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair torn tissues and alleviate symptoms. Accurate diagnosis is crucial, as sports hernias are often underreported and may be confused with other groin injuries like inguinal hernias, which can cause visible swelling and require different treatments.
If you participate in sports involving frequent twisting and turning and experience persistent groin pain, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended. Early intervention can prevent worsening of the injury and facilitate a quicker return to activity.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Genetic Mutation Influences Iron Deficiency in Crohn's Disease Patients
A groundbreaking study reveals how genetic mutations in PTPN2 impair iron absorption, leading to anemia in Crohn's disease patients, paving the way for personalized therapies.
CRISPR Research Identifies Mitochondrial Dysfunction as an Early Indicator in ALS
New CRISPR-based research uncovers mitochondrial dysfunction as an early indicator of ALS, highlighting potential targets for early intervention and treatment strategies.
Indigenous Researcher Revitalizes Traditional Medical Practices of His Community
A Pataxó Indigenous ethnobotanist is pioneering the documentation and revival of his community’s traditional medicinal practices, highlighting the importance of cultural preservation and sustainable health solutions.