A Mathematical Approach Illuminates the Placenta's Function and Significance
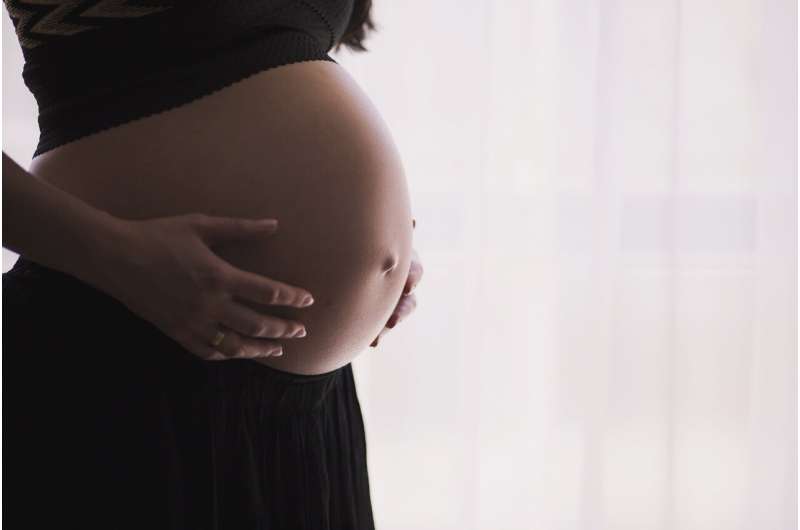

Emerging research uses advanced imaging and mathematical modeling to better understand the placenta's role in pregnancy, offering potential for early detection of complications like preeclampsia.
Pregnancy involves numerous medical assessments to ensure the health and wellbeing of both mother and baby, with particular attention to the placenta, an essential organ that supports fetal development. Typically, ultrasound scans check the placenta's position at around 20 weeks, but beyond that, detailed examinations are uncommon. However, recent research by biomedical engineer Pascalle Wijntjes highlights the importance of understanding the placenta's complex structure and functions in predicting pregnancy complications.
Wijntjes has devoted her doctoral research to mapping and modeling the placenta. Her work includes analyzing placental vascular systems and exploring how abnormalities may indicate risks such as preeclampsia. She emphasized that building accurate models requires a foundational understanding of placental anatomy and function, which is currently incomplete.
To gain deeper insights, Wijntjes employed advanced imaging techniques like contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and ultrasound localization microscopy (ULM). These methods involve injecting microscopic bubbles into the bloodstream, allowing observation of blood flow into tiny capillaries and detailed vessel mapping. The collected data has been used to create mathematical models that resemble branching trees, encapsulating the placenta's vascular complexity. These models are among the first of their kind worldwide.
Beyond simulating healthy placental blood flow, Wijntjes has also begun modeling abnormalities, such as narrowed blood vessels seen in conditions like preeclampsia. By adjusting parameters, she can study how such vascular changes impact blood flow to the fetus. Her ultimate goal is to develop a hybrid model that combines clinical data with physiological insights, providing a more reliable assessment of pregnancy risks.
Interestingly, Wijntjes' research coincided with her personal experience of pregnancy, which allowed her to witness placental growth firsthand through ultrasound scans. She acknowledges the challenge of maintaining professional boundaries but admits that her research has taken on new personal significance during her pregnancy.
This innovative work represents a significant step toward improved prenatal diagnostics, enabling early detection and management of complications, and underscores the potential of mathematical modeling and advanced imaging to unlock the secrets of the placenta’s vital yet complex role in pregnancy.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Salient Cues More Effective Than Episodic Future Thinking in Improving Children's Prospective Memory
Recent research finds that salient cues significantly outperform episodic future thinking in enhancing children's prospective memory, offering practical strategies for cognitive support.
Review Highlights Bone Health Risks Associated with Modern Cancer Therapies
Recent advances in cancer treatments have improved survival rates, but new research highlights the increased risk of bone loss and fractures associated with modern therapies. Experts call for proactive bone health management to protect long-term quality of life.
WHO Reports Nearly 100,000 Cholera Cases in Sudan Amid Escalating Crisis
The WHO reports nearly 100,000 cholera cases in Sudan amid ongoing conflict, displacement, and worsening health conditions. Urgent action is needed to address the outbreak and humanitarian crisis.
Need for Expanded Research on Racial, Gender, and Socioeconomic Disparities in Telestroke Care
Recent studies reveal that telestroke programs can help reduce racial, gender, and socioeconomic disparities in acute stroke treatment and recovery, but ongoing research is needed to address persistent inequalities.