Innovative Brain Injury Assessment Framework Promises Better Diagnosis and Treatment
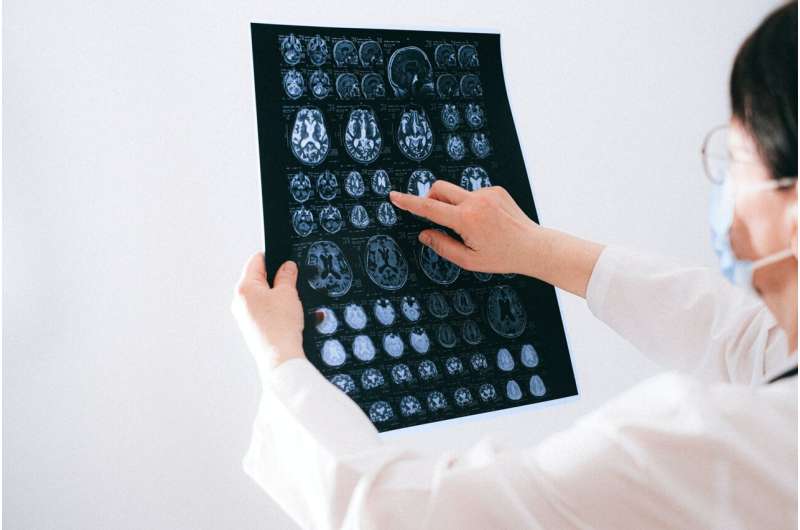
A new comprehensive assessment framework for traumatic brain injuries promises more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment, potentially transforming patient care.
A revolutionary approach to diagnosing and managing traumatic brain injuries (TBI) is on the horizon, marking a significant shift after more than 50 years. Led by a coalition of experts and patient advocates from 14 countries and sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, the new framework aims to provide more precise evaluation methods, which could lead to improved patient outcomes.
Traditionally, clinicians have relied on the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) for over five decades to categorize TBI severity into mild, moderate, or severe. However, this classification is often inadequate because it primarily assesses consciousness levels and a few clinical signs, ignoring other critical factors. As a result, some patients with severe injuries might not receive necessary aggressive care, while others with mild symptoms may be underestimated.
The updated framework, known as CBI-M (Comprehensive Brain Injury Model), introduces a multi-dimensional approach comprising four key components: clinical assessments, biomarkers, neuroimaging techniques, and injury modifiers. This comprehensive system is designed to create a more accurate picture of the injury's nature and severity.
Developed by expert working groups including over 100 professionals, patients, and researchers, the CBI-M framework incorporates blood-based biomarkers that serve as objective indicators of tissue damage. This allows clinicians to determine which patients can safely avoid unnecessary scans, thus reducing exposure to radiation and lowering healthcare costs. For patients with more serious injuries, imaging modalities like CT and MRI provide vital insights into bleeding, blood clots, and lesions, informing both immediate treatment and future care plans.
Currently, the framework is undergoing phased implementation at trauma centers for trial validation before full adoption. This advancement is expected to refine diagnostics, support personalized treatment strategies, and improve long-term outcomes for individuals affected by TBI.
For further details, see the full study published in the May 20 issue of Lancet Neurology. Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-05-traumatic-brain-injury-tool-aid.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Challenges in Implementing AI in NHS Healthcare: Insights from Recent UK Research
A recent UK study reveals the significant challenges faced in integrating AI technologies into NHS hospitals, highlighting the importance of strategic planning, staff training, and strong governance for successful digital transformation.
Innovative Zebrafish Study Offers Hope for Rare Lymphatic Disease Treatment
A groundbreaking study using zebrafish models uncovers potential drugs to treat kaposiform lymphangiomatosis (KLA), a rare lymphatic disorder, offering hope for faster, safer therapies.
Wastewater Surveillance as a Reliable Predictor of COVID-19 Community Infections
A University of Minnesota study confirms that wastewater testing for SARS-CoV-2 accurately predicts upcoming COVID-19 case surges, supporting proactive public health responses.



