Connecting with Nature: Green Neighborhoods Reduce Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
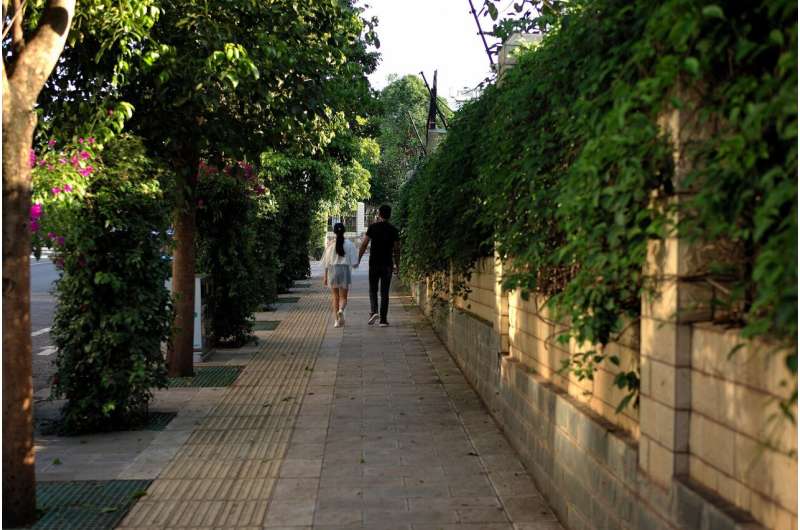

Living near abundant green spaces is linked to lower rates of smoking and daily alcohol consumption, with regular nature visits further promoting healthier behaviors across diverse populations.
A recent international study led by the University of Exeter highlights the positive impact of green spaces in residential areas on health-related behaviors. The research reveals that individuals living in neighborhoods with abundant vegetation and natural elements are less likely to smoke and engage in daily alcohol consumption. Specifically, people residing in the greenest neighborhoods are approximately 13% less likely to be current smokers and about 31% less likely to drink alcohol every day compared to those in less green areas.
This comprehensive study, part of the BlueHealth project and published in the journal Health & Place, analyzed data across 18 countries involving 18,838 adults from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Notably, the findings show that even moderate interaction with nature, such as visiting natural spaces at least once a week, is associated with healthier behaviors, including reduced smoking.
The research underscores that access to natural environments benefits all segments of society, regardless of income or education level. Lead researcher Dr. Leanne Martin emphasizes that these findings could be instrumental in public health strategies aimed at reducing harmful behaviors. By integrating green spaces into urban planning, communities may lower the prevalence of smoking and excessive drinking.
Furthermore, the study suggests that nature exposure influences cravings and stress levels, contributing to healthier choices. For instance, exposure to natural surroundings tends to promote calmness, reducing the need for substances like nicotine and alcohol. Dr. White from the University of Vienna comments that these effects could serve as valuable tools for interventions targeting health risk behaviors.
Overall, the findings advocate for increased investment in urban green spaces as a means to enhance public health and promote healthier lifestyles. Initiatives encouraging nature visits could be a vital part of community health improvement programs.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-05-people-nature-neighborhoods.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Study Shows Pulmonary Vein Isolation with Pulsed Field Ablation Similar in Effectiveness to Radiofrequency Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
A new study at ESC Congress 2025 shows that pulsed field ablation offers similar effectiveness to radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, with shorter procedure times and fewer complications.
Long-Term Weight Loss Continues After Tummy Tuck Surgery
New research shows that patients who undergo tummy tuck surgery may continue to lose weight for up to five years post-operation, highlighting the long-term benefits of the procedure for weight management.
Are Long-Term Health Risks Associated with Fecal Transplants?
Recent studies highlight potential long-term health risks of fecal microbiota transplantation, emphasizing the need for safer microbiome therapies and personalized approaches to gut health treatments.
Promising Results from Clinical Trial Using Immunotherapy and Radiotherapy for Leptomeningeal Disease
A recent clinical trial combining immunotherapy with radiotherapy shows promising survival benefits and immune response activation in patients with leptomeningeal disease, a serious complication of cancer.