Extreme Spring Pollen Levels in Europe Highlight Growing Allergy Concerns
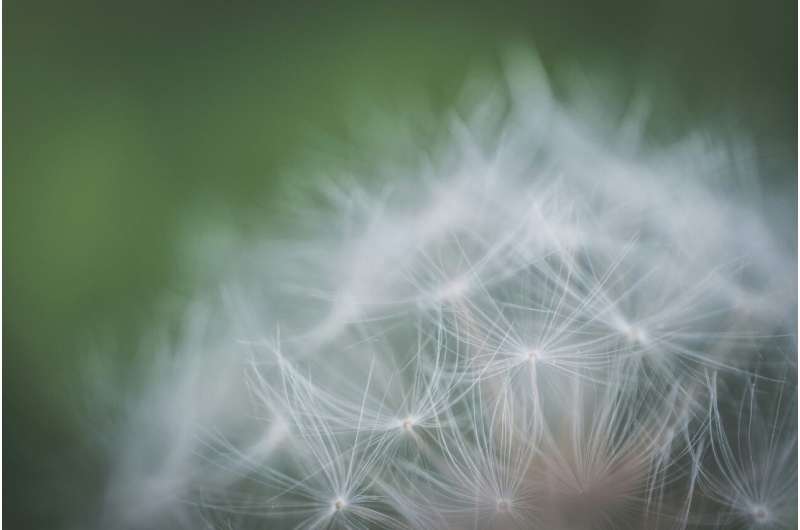

European regions are experiencing unprecedented high levels of pollen this spring, driven by climate change and environmental factors, increasing allergy and respiratory health risks across the continent.
During this spring, many regions across Europe experienced unprecedented levels of pollen, with some areas reporting "extreme" concentrations that affected even those without known allergies. Data from the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) indicated a notable increase in the release and transport of grass and olive pollen in southern Europe, as well as exceptionally high birch pollen levels in northeastern parts of the continent. Particularly in Finland, the situation was severe enough in May to cause allergy symptoms among individuals without prior sensitivities.
Climate change has been identified as a significant factor influencing these developments, as warmer temperatures and earlier thaws lead to prolonged and intensified pollen seasons. This results in more people experiencing allergy symptoms, which include hay fever and asthma exacerbations. Currently, about 25% of European adults suffer from airborne allergies, and this percentage could rise to half by 2050, according to WHO estimates.
Moreover, air pollution worsens allergy symptoms by increasing sensitivity to allergens. The spread of invasive plant and tree species into new regions also contributes to the growing prevalence of allergy-related issues.
In addition to pollen concerns, Europe faced significant wildfire events from March to May. Notably, April saw the UK's second-highest wildfire emissions since 2003, and the Netherlands reported unprecedented wildfire smoke levels. Fires in eastern Russia and Canada also impacted air quality, with smoke plumes reaching China, Japan, and Europe.
Experts highlight that while high pollen levels are typical in spring, this year's severity and widespread nature are particularly concerning. Continued environmental changes and wildfire activity are likely to further influence air quality and allergy prevalence in the future.
Source: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-07-pollen-extreme-europe-eu.html
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
Research Reveals Increased Fracture Risk After Discontinuing Hormone Replacement Therapy in Women
Discontinuing hormone replacement therapy in women leads to a rapid loss of bone fracture protection, with increased risk peaking around three years post-therapy. Ongoing bone health monitoring is essential for women after stopping MHT.
New Evidence Suggests ALS May Be an Autoimmune Disease Driven by Immune Cells Attacking Nervous System Proteins
Recent research suggests that ALS may be an autoimmune disorder, with immune cells mistakenly attacking nervous system proteins. This discovery opens new avenues for targeted therapies and improves understanding of disease progression.
Federal Cuts in Enforcement Staff and Suspension of Black Lung Disease Prevention Rules Impact Coal Miners' Safety
In 2025, federal agency staffing reductions and regulatory delays have compromised protections against black lung disease in coal miners, raising serious health and safety concerns amid ongoing legal and administrative challenges.
Modified DASH Diet Shows Promise in Lowering Blood Pressure for People with Type 2 Diabetes
A new study reveals that a modified DASH diet combined with sodium reduction can significantly lower blood pressure in people with type 2 diabetes, supporting dietary strategies for cardiovascular risk reduction.