Climate Change in Colorado's San Luis Valley Linked to Increased Kidney Disease in Agricultural Workers
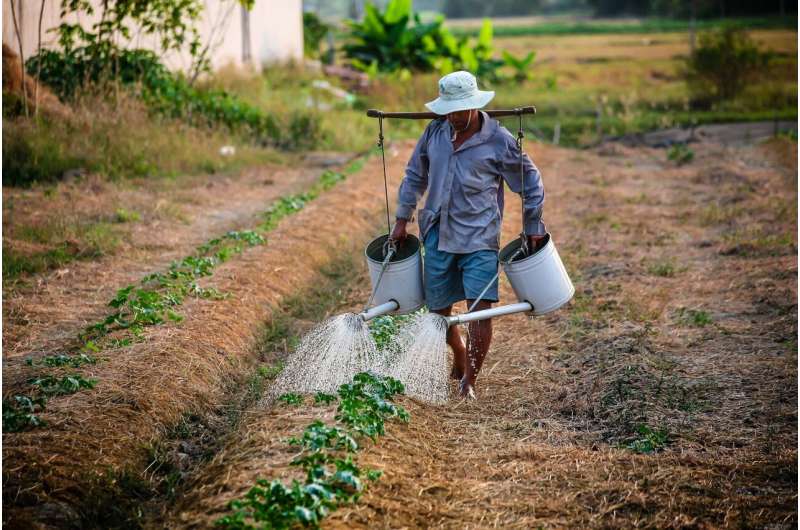

Recent research highlights the growing health risks faced by agricultural workers in Colorado's San Luis Valley due to climate change. Between 1984 and 1998, higher temperatures, increased humidity, and decreasing water availability contributed to a rise in kidney damage and disease among residents. The San Luis Valley, the largest high desert valley in North America, has experienced a significant shift toward drier conditions caused by a 23-year drought. These climatic changes, intensified by more frequent wildfires, dust storms, and soaring temperatures, have led to deteriorating air quality and heightened health concerns.
Many residents work outdoors, exposing themselves to worsening air pollution and extreme weather. The region's climate becoming more arid has been linked to increased instances of dehydration, acute kidney injury, and chronic kidney disease, especially among those engaged in physically demanding outdoor labor.
A study utilizing data from a long-term cohort—originally recruited for research on type 2 diabetes—found that a 10% decrease in humidity correlates with a 2% higher risk of acute kidney injury, even when accounting for other factors like age, sex, diabetes, and hypertension. Previous investigations have documented similar effects, such as increased emergency visits related to kidney issues during heat and drought periods.
Globally, about 10% of the population suffers from kidney disease, and it ranks among the top causes of death worldwide. In the United States, over one in seven adults has chronic kidney disease, with many remaining undiagnosed. The combination of drought, heat, and dehydration disproportionately impacts outdoor workers—such as farmers, miners, and construction laborers—leading to both immediate and long-term kidney health problems.
Efforts are underway to address these health challenges, including initiatives to reduce exposure to poor air quality and improve water filtration in vulnerable regions. Ongoing research focuses on understanding how climate-related factors like heat, air pollution, and drought influence overall health, with the goal of informing policies that protect workers and at-risk communities worldwide.
Stay Updated with Mia's Feed
Get the latest health & wellness insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Related Articles
New Insights into Aggressive Blood Cancer and Potential Targeted Therapies
Recent research uncovers the role of the enzyme SETD1B in supporting aggressive AML growth, offering new possibilities for targeted epigenetic therapies against this deadly blood cancer.
Widespread Dental Fear Persists Despite Desire for Treatment
Recent studies reveal that a high percentage of adults experience dental fear, yet most are interested in accessible treatments. Innovations like app-based therapies and telehealth are expanding options to combat dental anxiety and improve oral health.